Complex Constructive Solid Geometry (CSG)
Keywords:
-
radiation, GORAD
Problem Description
This example illustrates how to set up complex geometries using CSG capabilities of RSim: boolean operations on them and creating arrays.
Opening the Simulation
The complex CSG example is accessed from within RSimComposer by the following actions:
- Select the New → From Example… menu item in the File menu.
- In the resulting Examples window expand the RSim for Basic Radiation option.
- Expand the Basic Examples option.
- Select Complex Constructive Solid Geometry and press the Choose button.
- In the resulting dialog, create a New Folder if desired, and press the Save button to create a copy of this example.
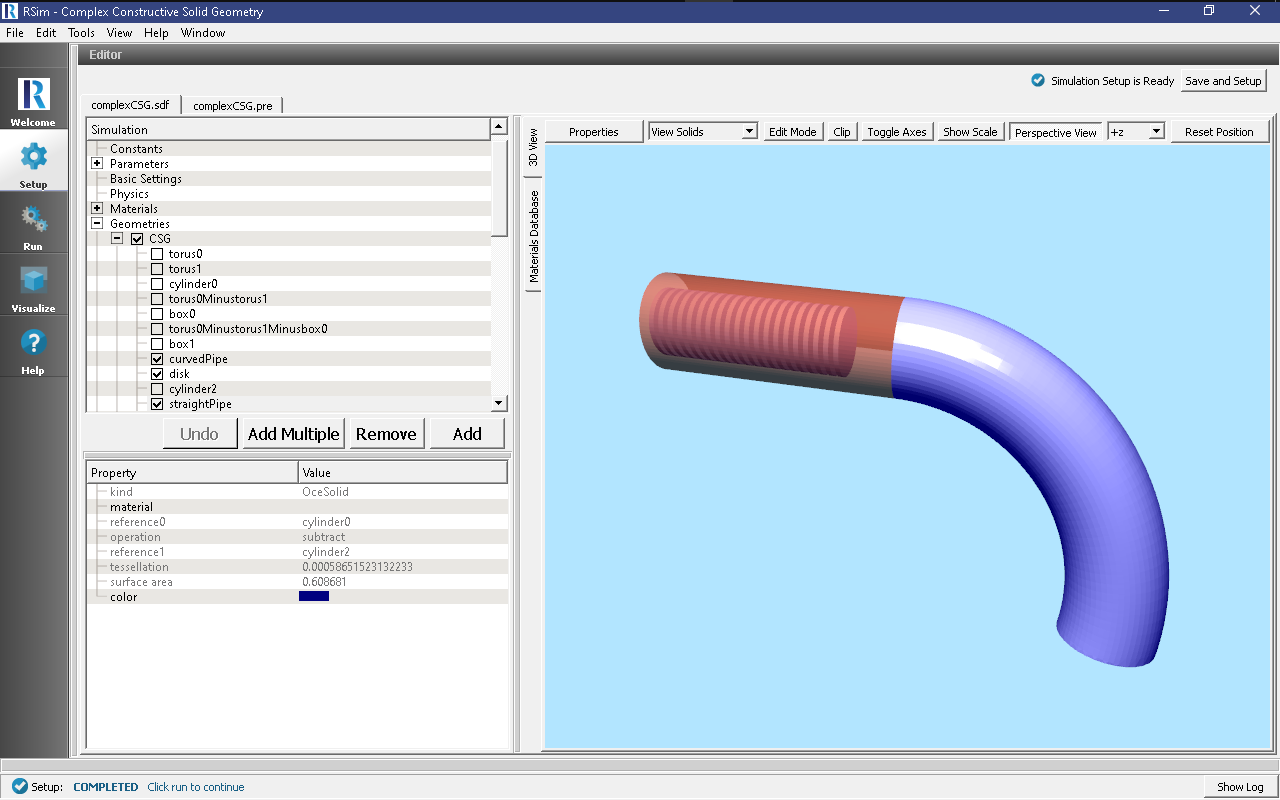
All of the properties and values that create the simulation are now available in the Setup Window as shown in Fig. 48. You can expand the tree elements and navigate through the various properties, making any changes you desire. The right pane shows a 3D view of the geometry, if any, as well as the grid, if actively shown. There are several shapes in the setup which are used only for creation of the boolean and array operations. They can be viewed in addition to the real shapes (shapes having materials).
Simulation Properties
This example demonstrates two physics features, and how CSG can be incorporated into RSim Simulations.
Under the Basic Settings tab the number of events to be simulated can be selected, as well as the simulation model. Right now the only supported model is GORAD.
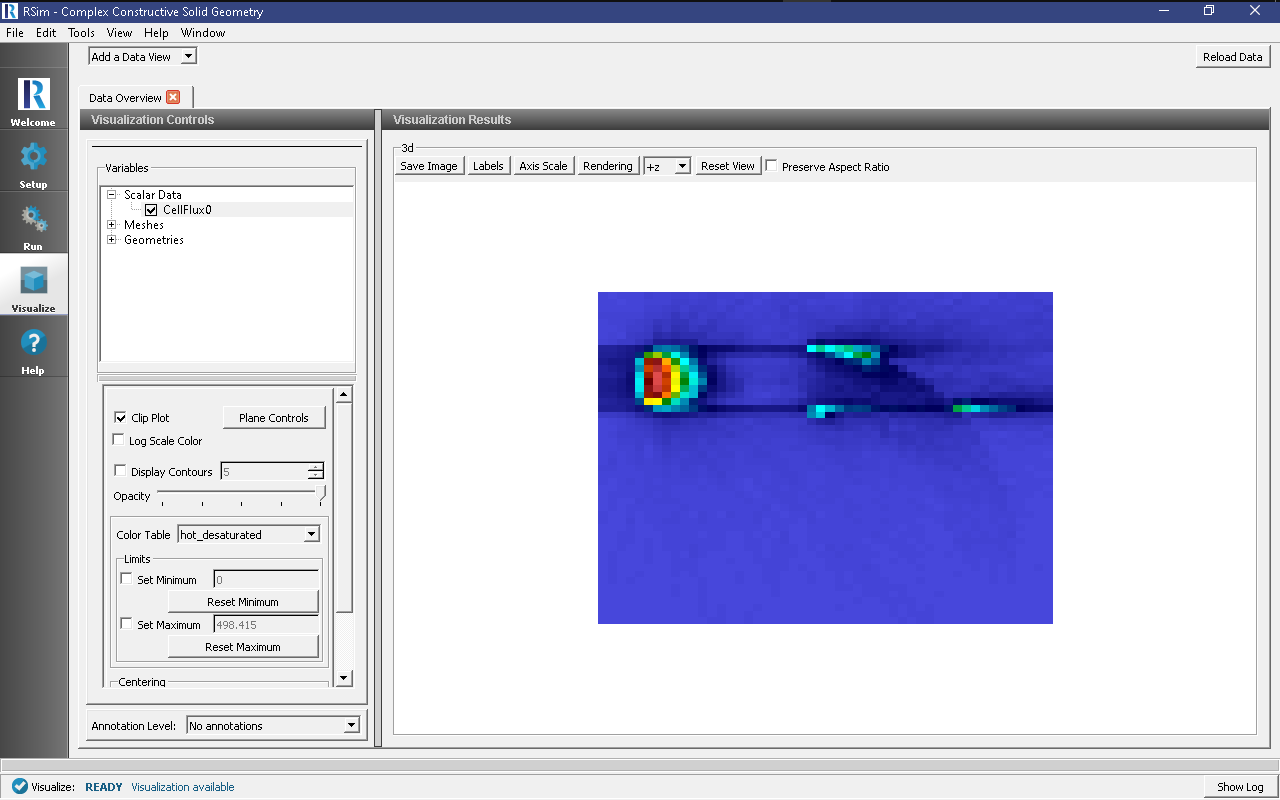
The particle source selected is a planar monoenergetic source with 1D beam shape. The tally in this simulation is is the mesh flux.
Running the Simulation
After performing the above actions, continue as follows:
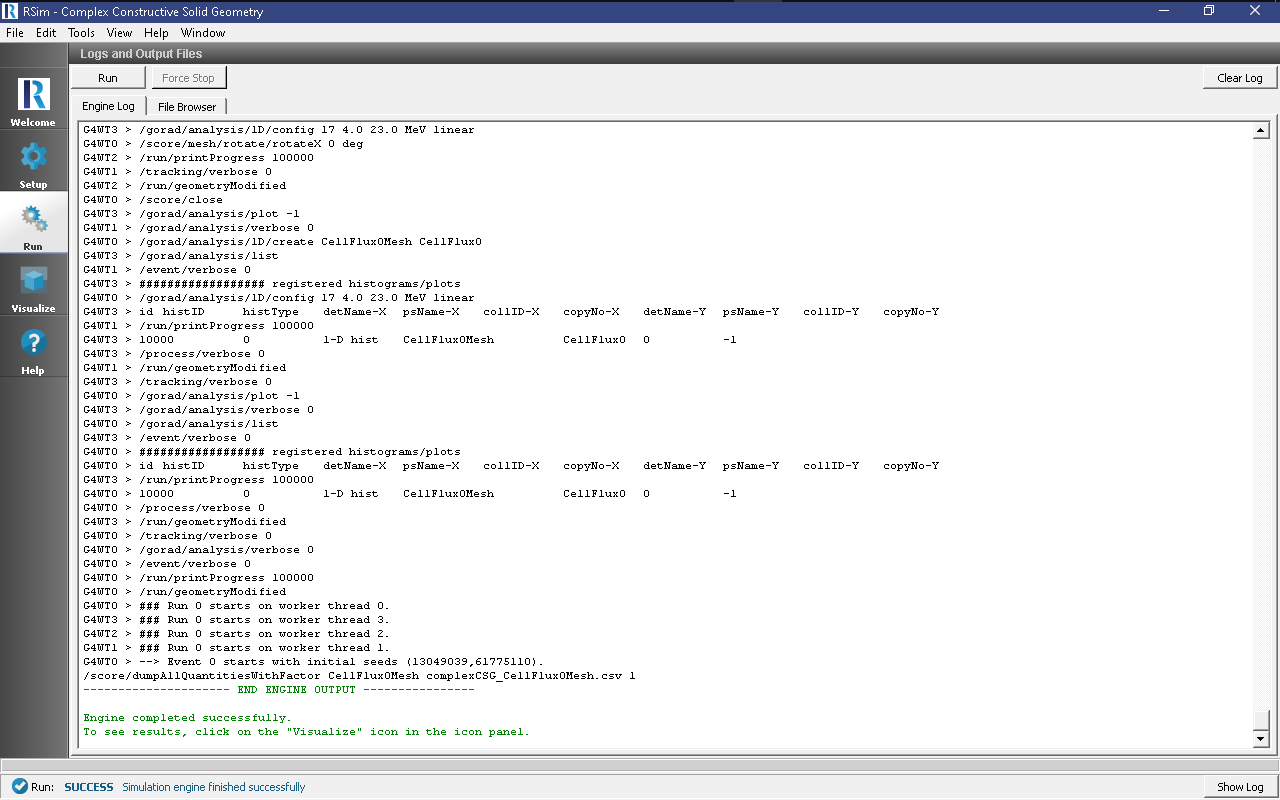
- Proceed to the Run Window by pressing the Run button in the left column of buttons.
- To run the file, click on the Run button in the upper left corner of the Logs and Output Files pane. You will see the output of the run in the right pane. The run has completed when you see the output, “Engine completed successfully.” This is shown in Fig. 49.