HDF5 Format Data Output Files
Vorpal outputs data in two forms, text and HDF5. Text output is
used for progress reporting, while HDF5 is used for data files.
The HDF5 data files have the .h5 suffix.
Hierarchical Data Format Version 5 (HDF5) is a library and file format for storing graphical and numerical data and for transferring that data between computers. Vorpal and VSimComposer output data in HDF5 format. The Hierarchical Data Format was developed by the National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. For more information about HDF5 (See http://hdfgroup.org/HDF5).
Dumping Fields, Particles, and GridBoundaries
The following are the general dumping options that can be set in field, particle, and grid boundary blocks. These can be used when the user wishes to customize the dumping options for the particular blocks and not change the global dumping options.
dumpOncePerRun (boolean)If true, this object will be dumped only once per run. This specification can co-exist with other specifications.
commandLineDumpPeriodicity (integer)This option may be automatically set by vorpal to override other attributes specifying when this object should dump its data.
dumpPeriodicity (integer)If dumpPeriodicity = p, then this object will be dumped to disc when its timestep mod p equals 0.
If p=0, this object ” “will never be dumped.
dumpPeriod (integer)(deprecated: please use dumpPeriodicity instead)
If dumpPeriodicity = p, then this object will be dumped to disc when its timestep mod p equals 0.
If p=0, this object will never be dumped.
dumpSteps (integer list)A list of the time steps at which this object should dump its data to disc.
dumpSteps (expression)A function of a scalar integer n (the current time step) that returns 1 if this object should be dumped at step n, and 0 if not.
To use an Expression, it must be specified within the <Expression dumpSteps> block:
expression = (a function of 'n', the timestep, that yields 0 or 1) For example, expression = ( mod(n, 100) == 0 ) or expression = ( or(n==100, n==200))
Vorpal produces one HDF5 file for each field or species at each
dump time. For example, if the simulation parameter
nsteps = 100 and the simulation parameter
dumpPeriodicity = 10,
Vorpal dumps data 10 times during the simulation and outputs a
total of 10 HDF5 files for each field or species while running
the simulation. Vorpal also produces one Globals file
at each dump containing data that is general to the whole
simulation, as opposed to one species or field. Finally, Vorpal
puts out a History file containing the data of the
specified histories.
Change the Names of Output Files
If you want to change the names of the output files, which include the .h5 files, you can specify the -o output option when you run Vorpal.
For example, you want to replace emPlaneWave with emPlaneWaveTest1
in the names of the emPlaneWave simulation’s output files. Run Vorpal
from the command line using this command:
vorpal -i emPlaneWave.in -o emPlaneWaveTest1
The output files will be:
emPlaneWaveTest1_all_1.txtemPlaneWaveTest1_comms_0.txtemPlaneWaveTest1_completed.txtemPlaneWaveTest1_dumpedobjs_0.txtemPlaneWaveTest1_electrons_1.h5emPlaneWaveTest1_Globals_1.h5emPlaneWaveTest1_SumRhoJ_1.h5emPlaneWaveTest1_YeeStaticElecField_1.h5
Displaying the Content of .h5 Files
The h5dump utility converts the binary data in
.h5 files into human-readable ASCII data in .txt
files, and is available for all the platforms on which Vorpal
runs. You can download the utility from the HDF5 website
(http://hdfgroup.org/HDF5).
The basic command is:
h5dump -o output_file_name.txt your_h5_file.h5
So, to convert the emPlaneWave_electrons_1.h5 to text format,
use this command:
h5dump -o emPlaneWave_electrons_1.txt emPlaneWave_electrons_1.h5
General Structure of Simulation Output .h5 Files
For each type of output file below, main data entries within that output file are displayed as a list of fields at the same level within the list. For those data fields within an output file that contain one or more subcategories of data, subcategories appear in an indented list below the main data category to which the subcategories apply.
Type of Output File: Globals
compGridGlobal
runInfo
time
Type of Output File: SumRhoJ
SumRhoJ
int array [NX NY NZ 4]
SumRhoJ[0] = Rho, charge density
SumRhoJ[1] = Jx
SumRhoJ[2] = Jy
SumRhoJ[3] = Jz
compGridGlobal
compGridGlobalLimits
runInfo
time
Type of Output File: Fluid
NeutralGasName
int array [NX NY NZ 1]
NeutralGasName[0] = Density
compGridGlobal
compGridGlobalLimits
runInfo
time
Type of Output Files: emMultiField – MagMultiField
MagMultiField
int array [NX NY NZ 3]
MagMultiField[0] = Bx
MagMultiField[1] = By
MagMultiField[2] = Bz
compGridGlobal
compGridGlobalLimits
derivedVariables
runInfo
time
Type of Output File: GridBoundary name
name
int array [NX NY NZ 2]
name[0] = true (1) or false (0) is the lower left front corner inside or not?
name[1] = true (1) or false (0) is the cell center inside or not?
nameLargeBndryFaces
nameLargeFaceFracs
nameSmallBndryFaces
nameSmallFaceFracs
nameStairStepBndryEdgesData
nameStairStepBndryFacesData
compGridGlobal
compGridGlobalLimits
derivedVariables
poly
runInfo
time
Type of Output File: History
runInfo
historyName1
historyName2
Note
These historyName arrays contain time data pertaining to the type of history chosen in the input file.
Type of Output File: species
species
int array [NX NY NZ 6]
species[0] = x position
species[1] = y position
species[2] = z position
species[3] = x velocity
species[4] = y velocity
species[5] = z velocity
compGridGlobalLimits
runInfo
time
Note
The information above is representative of 3D data. The actual number of elements in an array may vary depending on the dimensionality of the simulation. The number of elements in a species output file will also vary based on the type of species used. For more information on the output of species data, see the next section.
Columns in Particle Simulation .h5 Output Files
Below is a table displaying how the columns in particle simulation .h5
output files for various species kinds correspond to the columns that
can be seen in the .h5 file when the file is opened using a tool such as
HDFView. HDFView may be downloaded for free from the HDF Group at
http://www.hdfgroup.org/hdf-java-html/hdfview/. HDFView distributions
are available for 32-bit and 64-bit Linux, Mac, and Windows platforms.
| Species | Number of Columns | Comma-separated Columns |
|---|---|---|
| cmplxRelBorisDF | 5 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, real weight, imaginary weight |
| envBoris | 5 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag, weight |
| freeRel | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| freeRelVW | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| noMove | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| noMoveVW | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| nonRelBoris | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| nonRelEs | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| relBoris | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| relBorisBallisticVW | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| relBorisCyl | 3 + NDIM | u0,[u1,[u2,]]P0, P1, P2 (see Legend) |
| relBorisDF | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| relBorisEffMassExtd | 2 + 3(NDIM always 3) | x, y, z, Px, Py, Pz, valley index, weight (always 1) |
| relBorisFuncVW | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| relBorisTagged | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag |
| relBorisVW | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| relBorisVWTagged | 5 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag, weight |
| relBorisVWScale | 6 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag, scale parameter, weight |
| cell | 3 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz |
| cell(VW) | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, weight |
| cell(tagged) | 4 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag |
| cell(VW, tagged) | 5 + NDIM | x,[y,[z]]Px, Py, Pz, tag, weight |
Note
The cell species (kind = cell) set variable weight (VW) and tagging with
the variableWeightParticle and taggedParticle parameters.
| NDIM | Number of Dimensions: 1, 2, or 3 | |
|---|---|---|
| Dimension Notation | ||
| 1D | 2D | 3D |
| x | x y | x y z |
| 1D | 1D,[2D] | 1D,[2D,[3D]] |
| Cylindrical Coordinates | ||
| Polar | u0, u1, u2 | r, phi, z |
| Cylindrical | u0, u1, u2 | z, r, phi |
| Tubular | u0, u1, u2 | phi, z, r |
| Momentum/Mass Notation Convention | ||
| momentum/mass = gamma*v = P | ||
| gamma*vx:Px | gamma*vy: Py | gamma*vz: Pz |
HDFView Example Simulation .h5 Output File Illustration
Below are HDFView displays of Vorpal field and species
.h5 output files from an example simulation, as well as
brief descriptions of said output. HDFView may be downloaded for
free from the HDF Group (http://www.hdfgroup.org/hdf-java-html/hdfview/)
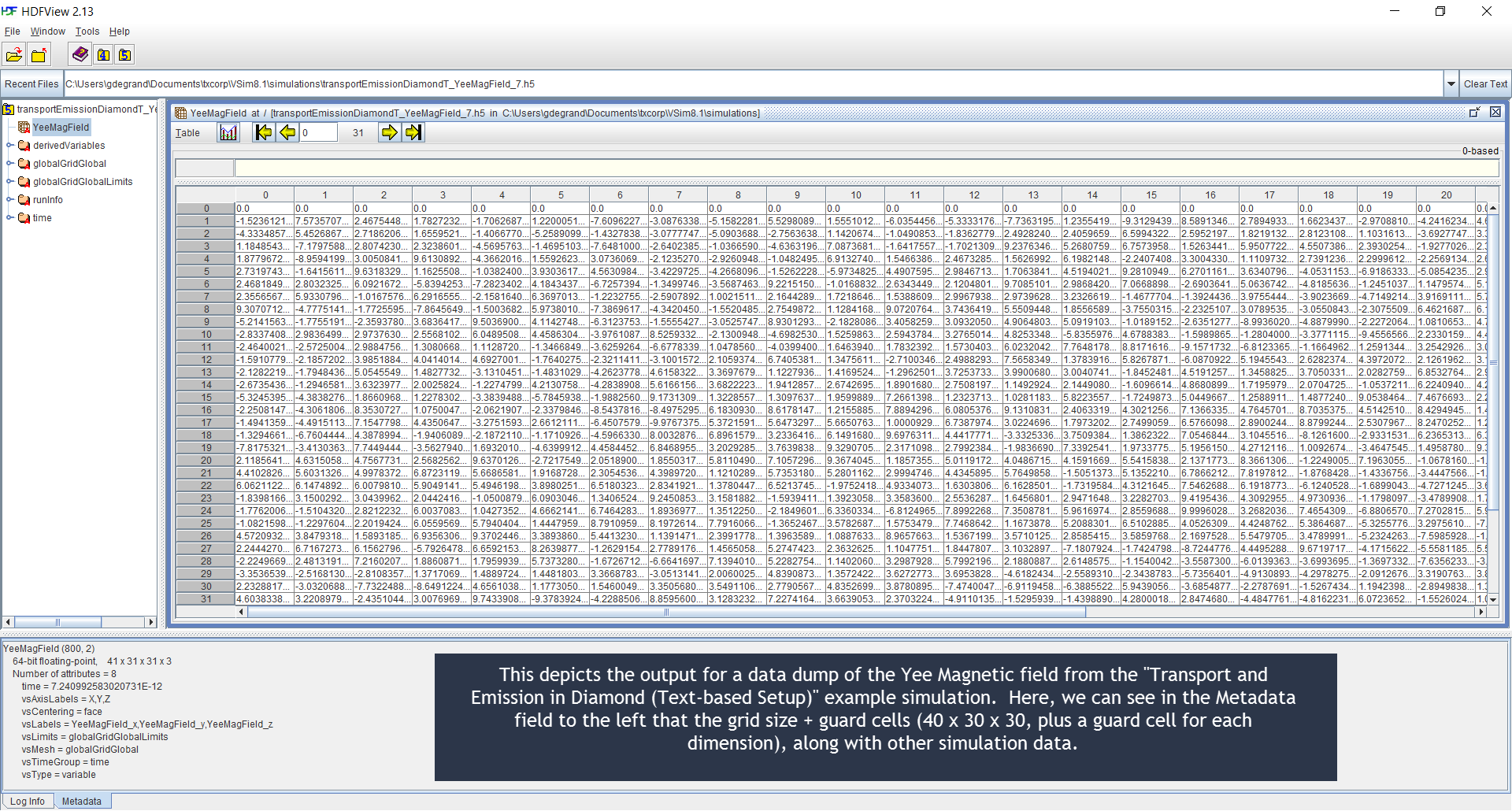
Fig. 95 HDFView display of a field file.
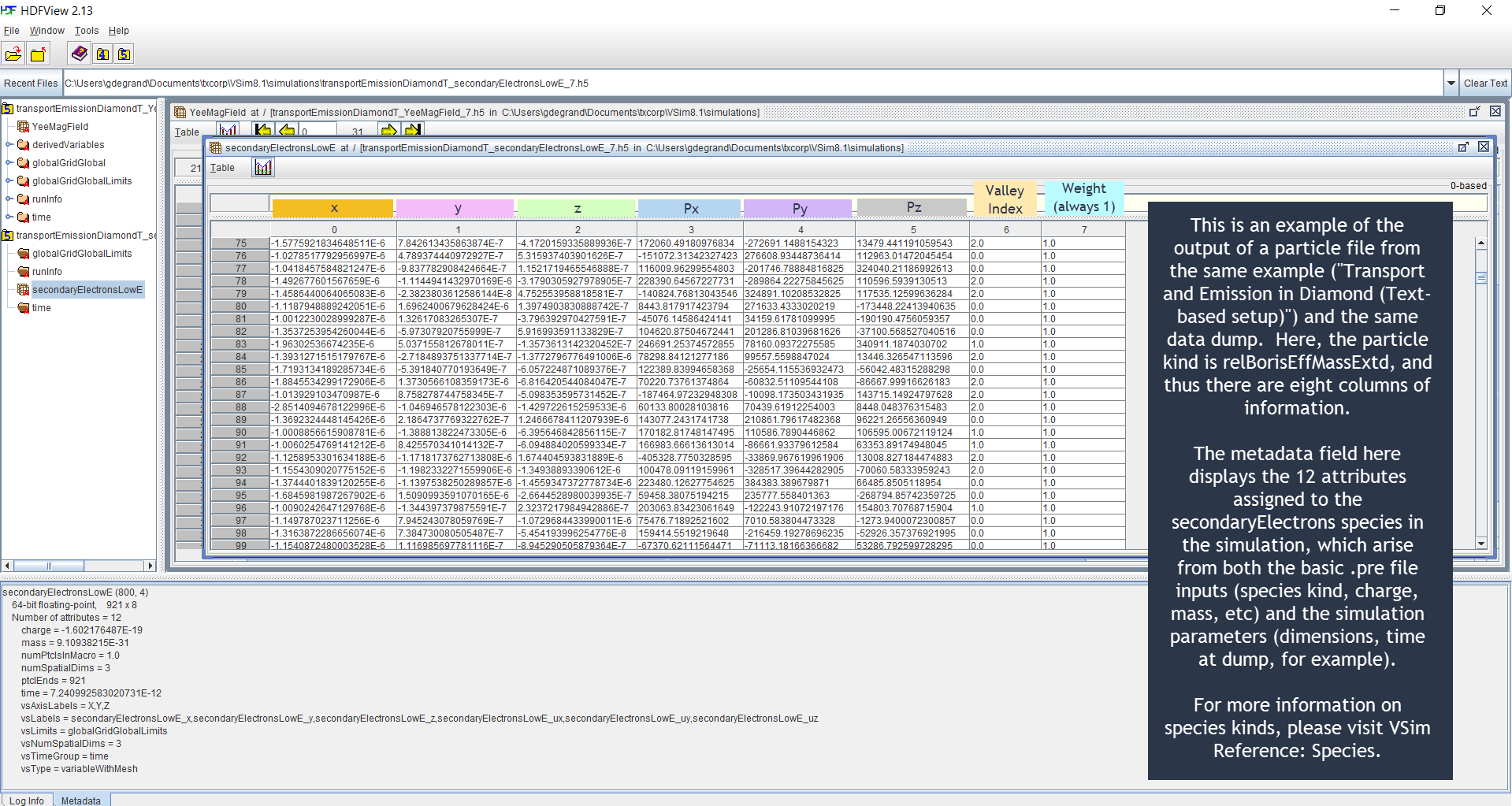
Fig. 96 HDFView display of particle file.